The truffles
All you need to know to make the most of the precious underground mushroom.
What is truffle?
Botanical origins, reproduction and physical characteristics
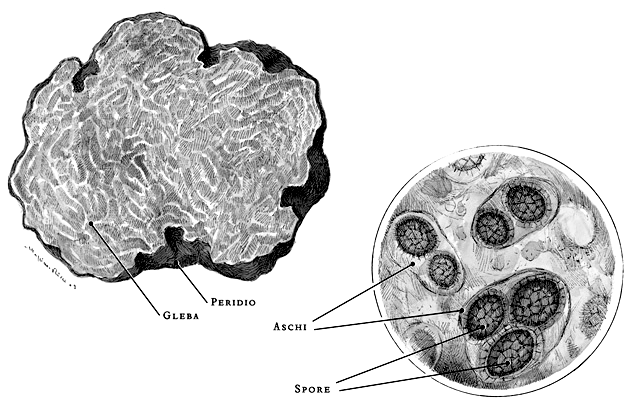
Botanically, truffles are particular mushrooms belonging to the genus Tuber, division Ascomycota, order Pezizales, family Tuberaceae.
Fungi or mycetes are organisms characterized by the lack of differentiated tissues (such as protozoa), which reproduce through spores and – being completely devoid of chlorophyll – which are unable to feed themselves by synthesizing inorganic molecules.
They are divided into two categories: saprophytes, which attack and degrade non-living substances of animal or vegetable origin, and mutualistic or symbiotic fungi, which live at the expense of other species, but reciprocate their hospitality by yielding in turn useful substances.
Species of the genus Tuber are fungi that, symbiotically associated with arboreal plants, complete the entire life cycle underground (underground).
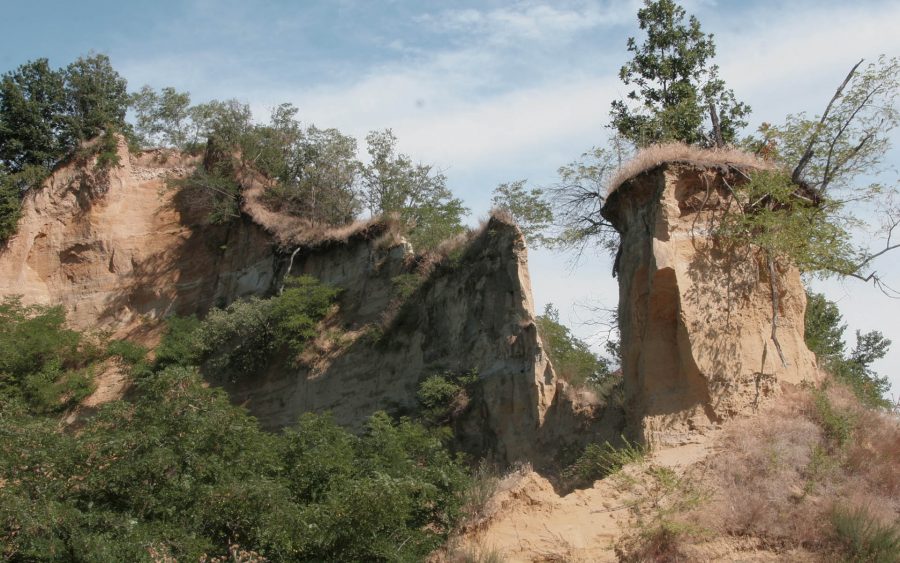

The history
Babylonians, Romans, the banquets of the Renaissance: let’s retrace it together
The strong and rooted presence of truffles in the traditions of Roero, Langhe and Monferrato and the passion that drives the searchers – called in Piedmontese “trifulau” – to venture, with their faithful and infallible dogs, on a hunt for this beloved and mysterious mushroom, lead us to delve into its history.
A frank product of the earth, which requires minimal intervention to be made edible, truffles have always exerted great fascination both for what concerns the strictly botanical aspect and for its use in the culinary field.
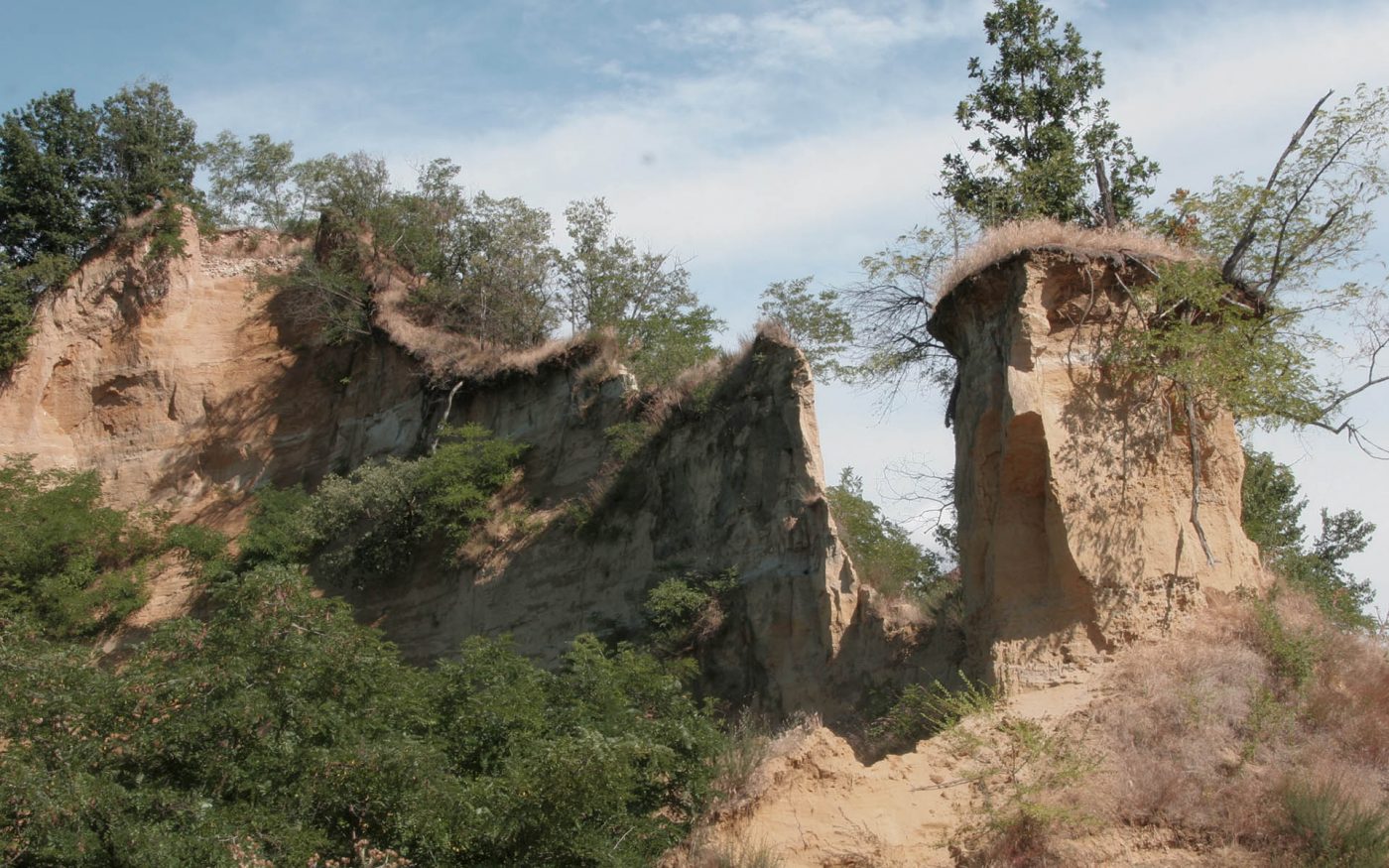
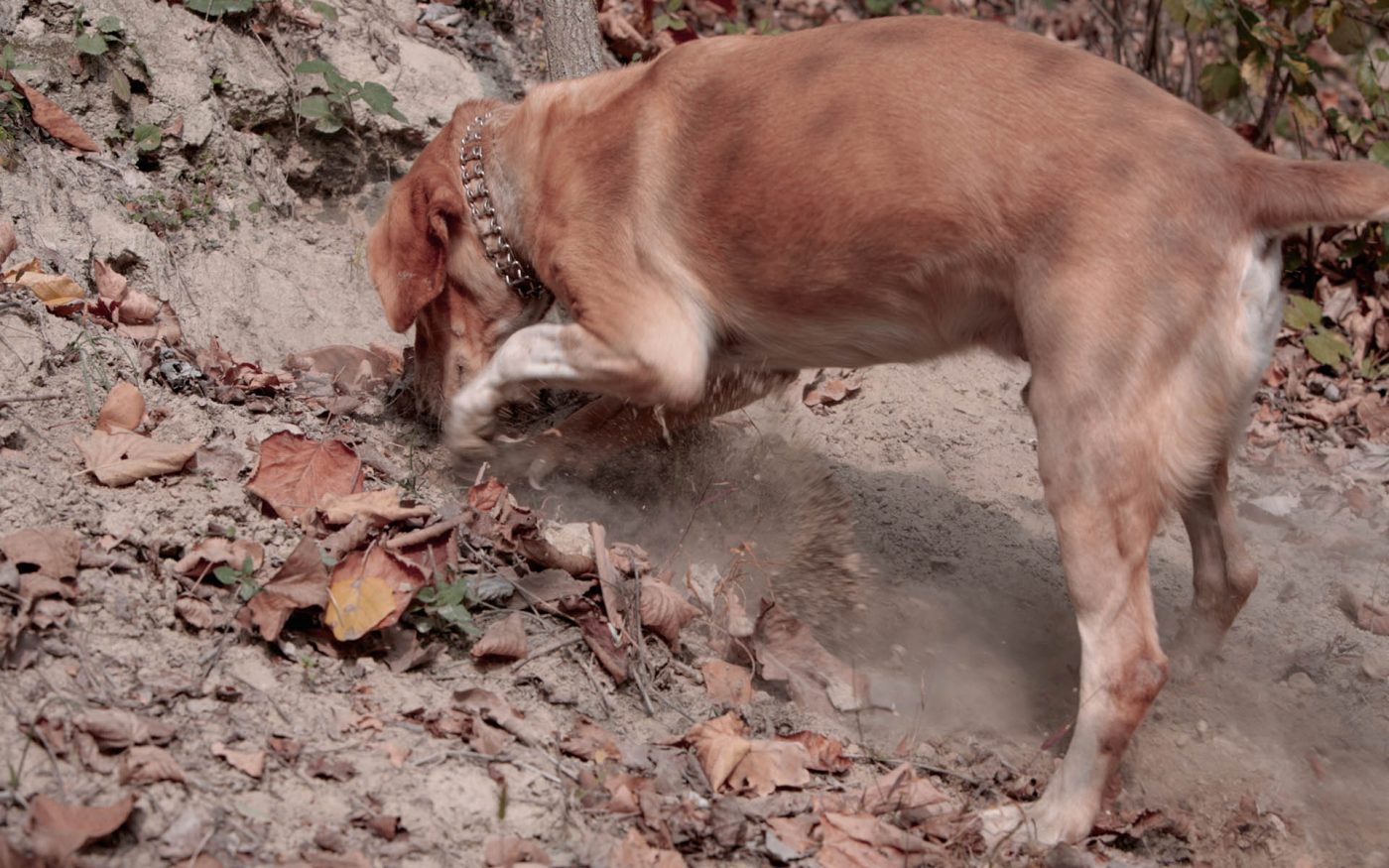


The truffle search
A man and his faithful dog, the woods and the hills, a timeless passion
In Piedmont the truffle hunter is called, in dialect, “trifulau”, “trifolao” or “trifulè” (hence the name of our company “Dal Trifulè” (which literally means “at the searcher’s place”).
The hunter must possess some fundamental skills for a fruitful search, including: excellent knowledge of the territory in which he moves, observation skills, the intuition in recognizing the best places, skilled hands when it comes time to extract the truffle from the soil and above all a good dog and an excellent understanding with the latter.
The activity is often carried out at night, partly to remain hidden from other seekers with the favor of the dark, partly because during the day they have a regular job.
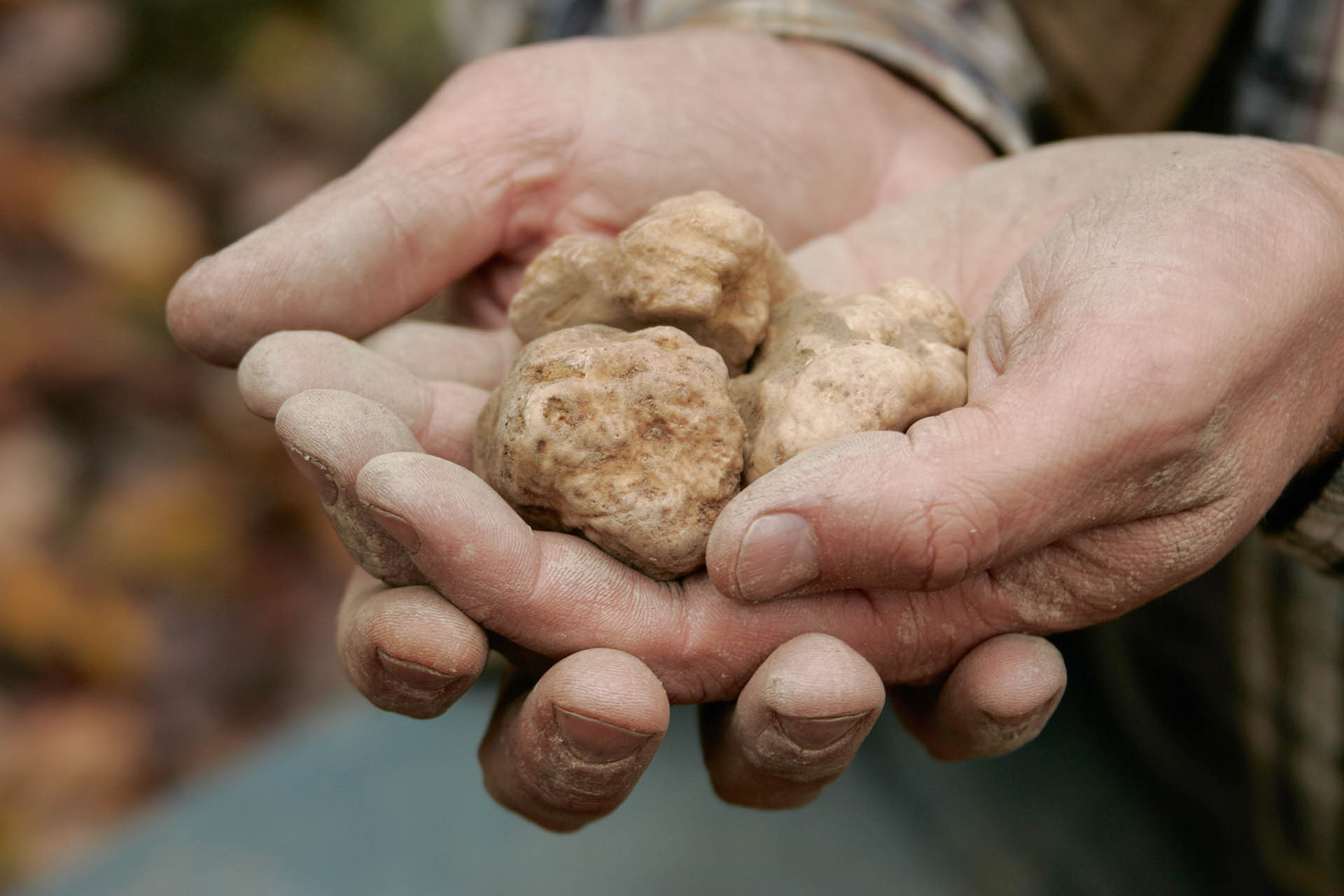

Advice on purchase and consumption
A precious ingredient, which at the same time is very delicate: find out how to enhance it
Buying truffles is an exciting moment, as is its consumption; however, there are many factors to keep in mind in order not to run into scams, to keep it at its best and not to ruin it in the kitchen.
It is in fact an ingredient of the highest value, but at the same time extremely delicate, which must be treated properly from the first encounter to the last taste to best extract its incredible goodness.
As experts of this precious mushroom we want to share all the secrets of the trade: starting from choosing the freshest one, going through the best preservation method, up to suggestions on how to pair it with food.

The varieties
Aesthetic and organoleptic differences: learn to recognize them.
In the different species the truffle is more widespread than you think. More than one hundred varieties of truffles are currently known, of which 63 are classified as Tuber. In Italy there are 25, but only 9 of them are recognized as edible by law.
From the biological and morphological point of view, as well as organoleptic, the Tuber species present significant differences between them.
The determination of the different species of truffles is essentially based on morphological characters such as shape, size, color, ornamentation of the peridium, appearance of the gleba (pulp), aroma and flavor.
The determination of the species in the laboratory, on the other hand, takes place through the recognition of the spores or with biomolecular analysis techniques.
